The Eight Standards of Curriculum 2013 in Indonesia - Current significance of Indonesia's curriculum emphasizes the improvement of eight standards of national education to achieve the main and most comprehensive vision i.e., societal goal.
Generally, we have known that most of all country has adherence to the certain societal goal. The term of societal goal used in this discussion refer to Posner, George J (1992:75) perspective that stated "societal goals are not primarily educational aims or goals, because they do not refer to outcomes achievable through learning; however almost any societal goal has some educational dimension." In other words, the term between educational and societal has different concern and dimension of mechanism, but it might become able to mutually supportive such as portrayed in the figure 1.0 bellow.
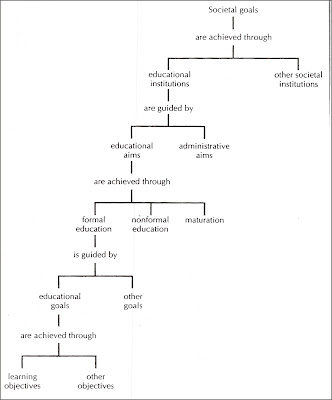 |
| Figure 1.0: The societal goal and educational goal |
Picture obtained on Posner, George J. (1992:76) Analyzing Curriculum.
C-13 or Curriculum 2013 is the mechanism or part of the educational system of Indonesia to achieve its particular societal goal. Indonesia's societal goals itself are contained in the preamble of constitutions 1945 which stated comprehensively i.e., to preserve national and global state unity; improve social mobility and educational frame. Henceforth, educational dimension is being involved to be participated to interpret the societal goal of education matter through educational institutions.
According to MENDIKBUD (Education and culture minister of Republic Indonesia) regulation number 69/2013 about structure and basic framework of curriculum in point of the C-13 rationale, it can be conceived that the problematic embodied in the education of Indonesia are based on two factors—first is internal adversity that refer to standard of process (i.e., Inefficient technical of instructional activity, and stagnant outcome.); standard of content (i.e., Particular irrelevant extension of the competencies characteristic with the current national demands.); standard of assessment (i.e., Incomprehensive instrument of assessment.); standard of educator and educational staff (i.e., Poor level efficiency of certain educator on a competence basis of the curriculum implementation and development.); standard of facility and infrastructure; standard of management; standard of finance (i.e., Ineffectiveness between supporting elements and operational elements on a reciprocal utilization basis.), and transformation attempt of productive age escalation which will attain its peak in 2020 until 2035. Second is external adversity that relate to globalization in environmental concerns; technological advances and information; creative and cultural industries, and the development of education on international extent.
The Eight Standards of Curriculum 2013 in Indonesia
The aforementioned adversity is the resources for the government of education to establish the primary element (i.e., Standard of competency outcome.) so that embody the improvement of two elements that function as supportive and operational. (See figure 1.2)
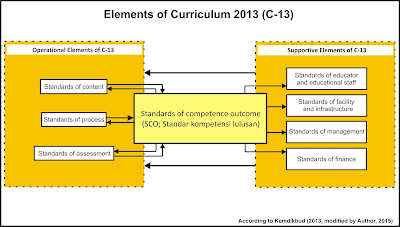 |
| Figure 1.2: The elements of Curriculum 2013 Observed by Author |
The first element is the SCO (Standards of competence outcome) which contains the criteria of qualification of the intended outcomes as the basis for the two types of elements (i.e., operational elements and supportive elements.). The operational element consist of ‘standard of content’ which contains the level of competence and characteristic of competences that intended to result in accordance with four domains of learning (i.e., religious attitudes, social attitude, cognitive, and psychomotor.), standards of process contains the characteristic of instructional, instructional planning, instructional implementation, etc—In order to attain the SCO in accordance with the level of education institutions. Henceforth, the characteristic of the instructional activity uses the level of cognitive domains, affective, and psychomotor as presented bellow in the table 1.0 (i.e., Sequenced in low order thinking (LOT) into high order thinking (HOT).), and standard of assessment contains the mechanism of evaluation which comprehensively formulated with the three domains of learning i.e., affective, cognitive, and psychomotor. For example, affective domain uses observation instrument that consist list of the intended behavior, cognitive domain uses multiple choices, essay, matching, etc, and psychomotor domain uses performance assessment such as practical test instrument i.e., check list, rating scale instrument which consist certain criteria. Finally, as we can see the supportive element, it consists of standard educator and educational staff, standard of facility and infrastructure, standard of management, and standard of finance. This supportive element has a role to support the operational element implementation in order to attain the SCO (Standard of competence outcome).
| AFFECTIVE | COGNITIVE | PSYCHOMOTOR |
|---|---|---|
| Receive | Remember | Imitation |
| Respond | Understand | Manipulation |
| Value | Apply | Develop Precision |
| Organize Personal Value System | Analize | Articulation |
| Internalize Value System | Evaluate | Naturalization |
| - | Create | - |
Table 1.0
REFERENCE
A. Journals
Marlina, Murni Eva. 2013. Kurikulum 2013 yang berkarakter. JUPIIS: Jurnal pendidikan ilmu-ilmu sosial, vol. 5, no. 2. Retrieved in March 8, 2014, from http://jurnal.unimed.ac.id/2012/index.php/jupiis/article/view/1112/882
B. State Documents
Government of republic Indonesia’s regulation number 32/2013 about amendment in regulation number 19/2005 about “Standards of national education”
MENDIKBUD regulation number 54/2013 about standards of competence outcome.
MENDIKBUD regulation number 59/2014 about senior high school curriculum.
MENDIKBUD regulation number 64/2013 about standards of content.
MENDIKBUD regulation number 65/2013 about standards of process in elementary and high school degree of education unit.
MENDIKBUD regulation number 66/2013 about standards of assessment in elementary and high school degree of education unit.
MENDIKBUD regulation number 69/2013 about structure and basic framework of curriculum in senior high school/madrasah aliyah degree of education unit.
MENDIKBUD regulation number 81A/2013 about the guidelines of curriculum implementation.
MENDIKBUD regulation number 160/2014 about the enforcement of curriculum 2006 and curriculum 2013.
C. Books
Posner, George J. 1992. Analyzing the curriculum. New York, USA: McGraw hill, Inc.
Suherdi, D. 2012. Towards the 21st century English teacher education: An Indonesian perspective. Bandung, IDN: Celtics Press.
Widyastono, H. 2014. Pengembangan kurikulum di era otonomi daerah: Dari kurikulum 2004, 2006, ke kurikulum 2013. Jakarta, IDN: Bumi Aksara.
________. 2013. Menyambut kurikulum 2013. Jakarta, IDN: PT. Kompas media nusantara.
Related Post
Sign up here with your email